
Subscribe to Newsletter
We will send you news from PowerTech Systems on a regular basis.
Maximum one email per month
Please fill-in right form with your contact details and click "Register"
[sibwp_form id=1]
The lithium-ion battery sector is constantly evolving, with daily research aimed at improving battery performance, range, power and charge times.
Among recent technologies, solid-state batteries represent a major development for the future of electric mobility.
These batteries use a solid electrolyte instead of the liquid electrolyte of traditional lithium-ion batteries.
the video below details the operating principles of a solid-state lithium battery.
Les batteries à l’Etat Solide sont très prometteuses, notamment en termes de sécurité, de performance et de durabilité.
Mais pour parvenir à une production à grande échelle et à coûts maîtrisés, il faudra attendre encore quelques années.
Les enjeux technologiques sont tels qu’un certain nombre d’étapes restent à franchir, notamment en ce qui concerne la durabilité des électrolytes métalliques ou céramiques.
En attendant que les électrolytes solides détrônent les liquides, la recherche se concentre sur une technologie intermédiaire : les batteries semi-solides, avec des électrolytes polymérisés.
Les électrolytes polymérisés (également appelés électrolytes gélifiés) contiennent des conducteurs ioniques tels que les sels de lithium, qui permettent une conductivité ionique beaucoup plus efficace. La structure polymère résiste également à la formation de dendrites, des structures en forme d’aiguilles qui peuvent se former sur l’anode pendant la charge et provoquer des courts-circuits. En outre, les gels sont beaucoup moins volatils que les électrolytes liquides, et donc très difficiles à enflammer.
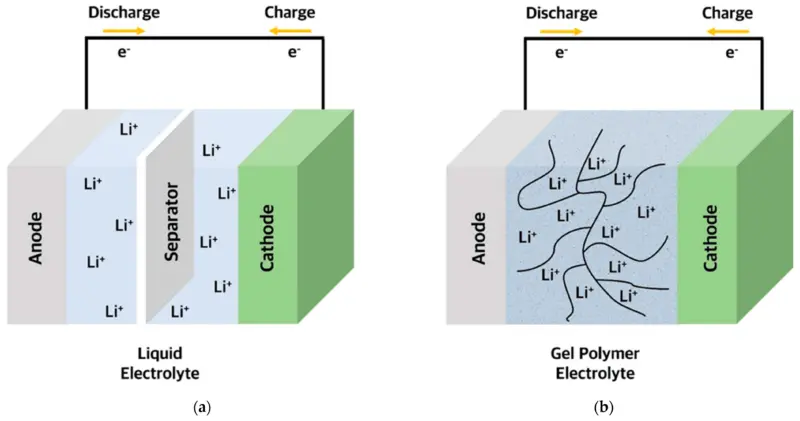
Although semi-solid-state batteries do not achieve the energy densities and lifetimes expected of solid-state batteries, they offer a medium-term advantage in that they can be manufactured on conventional lithium-ion battery production lines. Just as importantly, they have been tested and are now available on the market. On the other hand, Solid-state cells will be available at a reasonable cost by 2027-2028.
The energy density of semi-solid batteries is currently similar or slightly higher to that of standard LFP batteries, but all the other advantages of solid-state are already there. We can expect this lithium battery technology to gain momentum, with a major evolutionary step towards ever-increasing energy density in the years to come.
The future is already here: the new PowerModule SOLID-STATE product, equipped with semi-solid cells technology is already operational and available :